My Investment Declaration
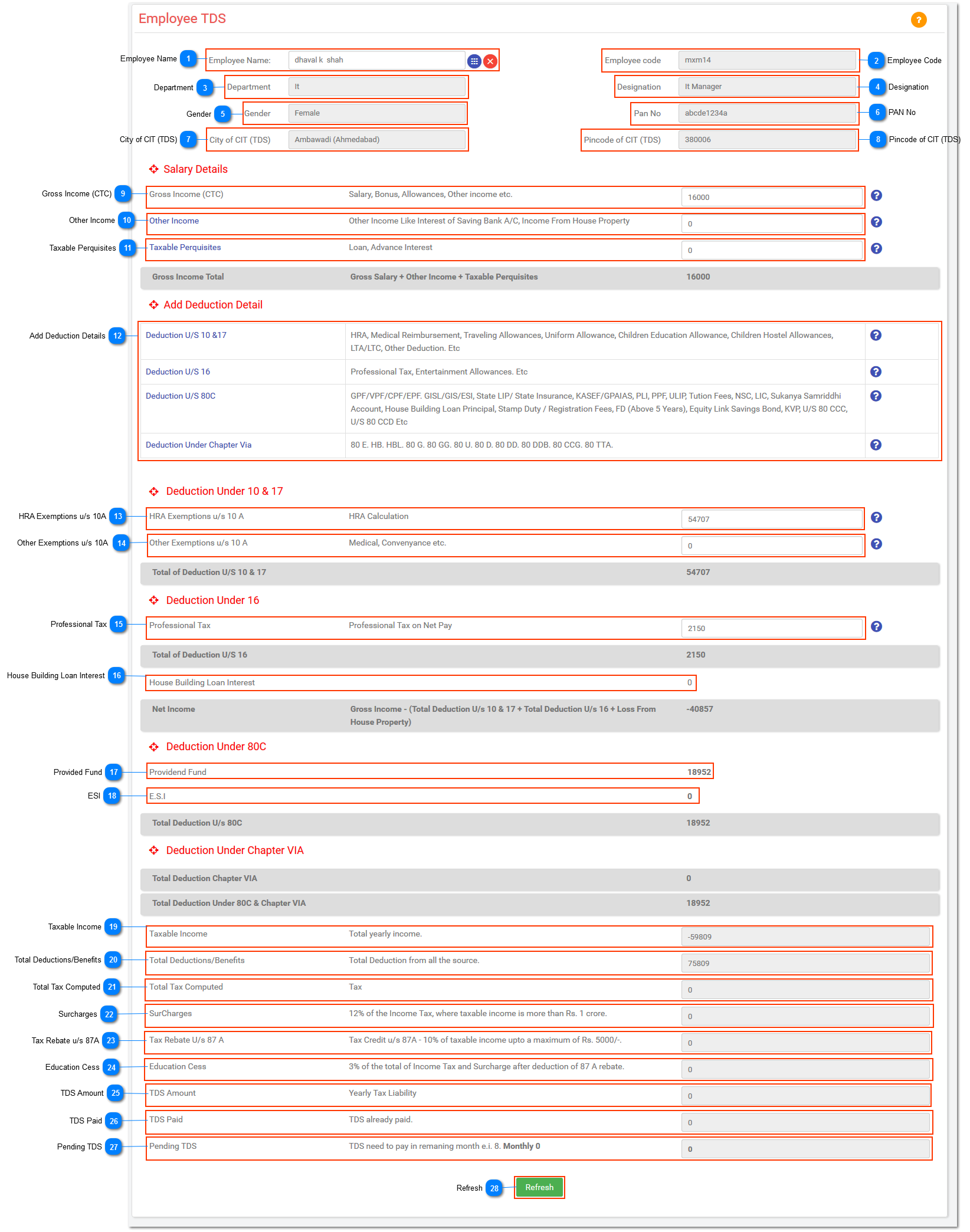
NOTE: Gross Income Total = Gross Salary + Other Income + Taxable Perquisites
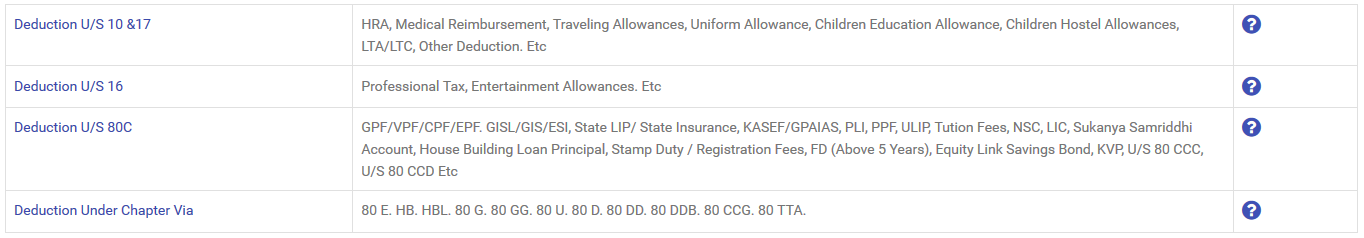 *Deduction U/ S 10 & 17: HRA
1) Employees generally receive a house rent allowance (HRA) from their employers. This is a part of the salary package, in accordance with the terms and conditions of employment. HRA is given to meet the cost of a rented house taken by the employee for his stay.
2) The Income Tax Act allows for deduction in respect of the HRA paid to employees.
3) The exemption on HRA is covered under Section 10(13A) of the Income Tax Act and Rule 2A of the Income Tax Rules.
4) It is to be noted that the entire HRA is not deductible. HRA is an allowance and is subject to income tax.
5) An employee can claim exemption on his HRA under the Income Tax Act if he stays in a rented house and is in receipt of HRA from his employer.
6) In order to claim the deduction, an employee must actually pay rent for the house which he occupies.
-->Medical Reimbursement.
1) Medical Reimbursement up to Rs. 15,000, If an employee receives some money for his medical treatment or the treatment of any member of his family or any of his dependant relatives then a sum up to Rs. 15,000 p.a. is not treated as a taxable perquisite as per Clause (b) of the provision to Section 17 (2) of the I.T. Act.
2) This exemption is enjoyed byte employee only if the expenditure is actually incurred on his medical treatment or for treatment of any member of the family or a dependant relative.
3) It may be noted here that there is no condition that the medical treatment should be at any of the approved hospitals.
4) It could be at any place and from any type of doctor belonging to Allopathic, Ayurvedic, Unani or Naturopathy system of medicine. If medicalallowance is received then it would be fully taxable.
-->Travelling Allowances.
1) Any allowance granted to meet the cost of travel on tour or on transfer of duty. “Allowances granted to meet the cost of travel on transfer” includes any sum paid in connection with transfer, packaging and transportation of personal effects of such transfer.
2) Uniform Allowance. Any allowance, by whatever name called, granted to meet the expenditure incurred on the purchase or maintenance of uniform for wear during the performance of duties of an office or employment of profit.
3) Children Education Allowance. The allowance is given for children's education.
4) Children Hostel Allowances. The allowance is granted to an employee to meet the hostel expenditure on his child.
5) LTA/LTC Leave Travel Allowance to employees can be claimed if an employee goes on a vacation. This Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) can be claimed when an employee goes on a vacation and submits the actual bills to the employer. This amount is also sometimes referred to as LTC (Leave Travel Concession)
6) Conveyance Allowance: Conveyance allowance is granted to meet expenditure on conveyance in performance of duties of an office. Exemption 1. Amount of the allowance or 2. The amount utilized for the specific purpose – whichever is lower.
7) Other Deduction.
*Deduction U/S 16:
1) Professional Tax.
2) Entertainment Allowances.
*Deduction U/S 80C:
The Government wants to encourage some certain types of investments and expenses. To achieve this goal it gives the benefit of tax deductions. There are many investments and expenses under section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD. However, the total deductions under this section are limited to Rs 1.5 lakh.
-->GPF/VPF/CPF/EPF.
1) For salaried employees GPF/VPF/CPF/EPF one of the deduction. If a company has twenty employees, under the rules of Govt. of India, you need to contribute 12% of your basic Pay including DA to EPF. The interest earned on EPF/VPF is tax free.
2) Employees can take loan against EPF and also do partial withdrawal under certain conditions. This is the best convenient option to invest as the amount is deducted from salary.
-->GISL/GIS/ESI.
-->State LIP/ State Insurance. Life Insurance Premium: In case of individual, on life of assessee, assessee’s spouse and any child of assessee.
-->KASEF/GPAIAS.
-->PLI.
-->PPF. Salaried employee and self-employed person, PPF is one of the option. Maximum investment under this is allowed Rs: 1.5 lakh per year. For keep the account active minimum investment Rs: 500 are required every year.
-->ULIP. Unit Linked Insurance Plan which is combination of life insurance and equity investments. For hefty commissions (70% in first premium) in the ULIP the agents were pushing the scheme to the people. There are other investment options which can yield the same gains.
-->Tution Fees.
-->NSC. NSC is TAX saving fixed deposit scheme which you can get from Post offices. Tax payer can avail deduction is only maximum 1lakh.
-->LIC.
-->Sukanya Samriddhi Account. Contribution to Sukanya Samriddhi Account Opened in the Name of Daughters.
-->House Building Loan Principal. An individual having home loan, can claim the principal repayment as deduction under section 80C. The deduction up to Rs 1, 00,000/- is allowed on the principle repayment of the housing loan is self-occupied or vacant. The deduction for interest incurred on principal can be deductible under Section 24 of the Income Tax Act.
-->Stamp Duty / Registration Fees.
FD (Above 5 Years). Payment made as five year time deposit in an account under the Post Office Time Deposit.
-->Equity Link Savings Bond.
-->KVP.
-->Other Deduction.
-->U/S 80 CCC Section 80CCC: Deduction for Annuity Plan: Payment of premium for annuity plan of LIC or any other insurer Deduction is available upto a maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/ The premium must be deposited to keep in force a contract for an annuity plan of the LIC or any other insurer for receiving pension from the fund. The Finance Act 2015 has enhanced the ceiling of deduction under Section 80CCC from Rs.100, 000 to Rs. 1, 50,000 with effect from A.Y. 2016-17
-->U/S 80 CCD Deposit made by an employee in his pension account to the extent of 10% of his salary. 2015-2016 or Assessment Year (2016-2017), this will be Rs 1.5 Lakh (u/s 80 CCD 1 ) and additional exemption of Rs 50,000 u/s 80CCD (1b) will be allowed. (To claim this deduction, the employee has to contribute to Govt recognized Pension schemes like NPS) (10% of salary is applicable for salaried individuals and Gross income is applicable for non-salaried. The definition of Salary is only ‘Dearness Allowance.’ If your employer also contributes to Pension Scheme, the whole contribution amount (10% of salary) can be claimed as tax deduction under Section 80CCD (2). The ceiling limit of 1.5 Lakh u/s 80CCD is not applicable on employer’s contribution.)
*Deduction Under Chapter Via:
The Government wants to encourage some certain types of investments and expenses. To achieve this goal it gives the benefit of tax deductions. There are many investments and expenses under section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD. However, the total deductions under this section are limited to Rs 1.5 lakh.
-->GPF/VPF/CPF/EPF.
1) For salaried employees GPF/VPF/CPF/EPF one of the deduction. If a company has twenty employees, under the rules of Govt. of India, you need to contribute 12% of your basic Pay including DA to EPF. The interest earned on EPF/VPF is tax free.
2) Employees can take loan against EPF and also do partial withdrawal under certain conditions. This is the best convenient option to invest as the amount is deducted from salary.
-->GISL/GIS/ESI.
-->State LIP/ State Insurance. Life Insurance Premium: In case of individual, on life of assessee, assessee’s spouse and any child of assessee.
-->KASEF/GPAIAS.
-->PLI.
-->PPF. Salaried employee and self-employed person, PPF is one of the option. Maximum investment under this is allowed Rs: 1.5 lakh per year. For keep the account active minimum investment Rs: 500 are required every year.
-->ULIP. Unit Linked Insurance Plan which is combination of life insurance and equity investments. For hefty commissions (70% in first premium) in the ULIP the agents were pushing the scheme to the people. There are other investment options which can yield the same gains.
-->Tution Fees.
-->NSC. NSC is TAX saving fixed deposit scheme which you can get from Post offices. Tax payer can avail deduction is only maximum 1lakh.
-->LIC.
-->Sukanya Samriddhi Account. Contribution to Sukanya Samriddhi Account Opened in the Name of Daughters.
-->House Building Loan Principal. An individual having home loan, can claim the principal repayment as deduction under section 80C. The deduction up to Rs 1, 00,000/- is allowed on the principle repayment of the housing loan is self-occupied or vacant. The deduction for interest incurred on principal can be deductible under Section 24 of the Income Tax Act.
-->Stamp Duty / Registration Fees.
FD (Above 5 Years). Payment made as five year time deposit in an account under the Post Office Time Deposit.
-->Equity Link Savings Bond.
-->KVP.
-->Other Deduction.
-->U/S 80 CCC Section 80CCC: Deduction for Annuity Plan: Payment of premium for annuity plan of LIC or any other insurer Deduction is available upto a maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/ The premium must be deposited to keep in force a contract for an annuity plan of the LIC or any other insurer for receiving pension from the fund. The Finance Act 2015 has enhanced the ceiling of deduction under Section 80CCC from Rs.100, 000 to Rs. 1, 50,000 with effect from A.Y. 2016-17
-->U/S 80 CCD Deposit made by an employee in his pension account to the extent of 10% of his salary. 2015-2016 or Assessment Year (2016-2017), this will be Rs 1.5 Lakh (u/s 80 CCD 1 ) and additional exemption of Rs 50,000 u/s 80CCD (1b) will be allowed. (To claim this deduction, the employee has to contribute to Govt recognized Pension schemes like NPS) (10% of salary is applicable for salaried individuals and Gross income is applicable for non-salaried. The definition of Salary is only ‘Dearness Allowance.’ If your employer also contributes to Pension Scheme, the whole contribution amount (10% of salary) can be claimed as tax deduction under Section 80CCD (2). The ceiling limit of 1.5 Lakh u/s 80CCD is not applicable on employer’s contribution.)
|
NOTE: Net Income = Gross Income - (Total Deduction u/s 10 & 17 + Total Deduction u/s 16 + Loss From House Property)
